Water-based cutting fluids are used more and more widely in today's machining industry. Excellent cutting fluid products, supplemented by good on-site maintenance, will help improve production efficiency, extend tank life, and make comprehensive costs more competitive. force. As a special medium for machining process, cutting fluid may have some common problems during use due to its own composition characteristics and external factors, such as insufficient lubrication, easy rust, non-ferrous metal corrosion, and long bacteria. In addition to odor, operator dermatitis, etc., in addition, the problem of resistance to hard water or soap accumulation has become a phenomenon that deserves attention. Water-based cutting fluids are almost inherently capable of forming soaps. On the one hand, there are a large amount of calcium and magnesium ions in water, and on the other hand, most of the cutting fluid formulations add fatty acids, which are easy to form fatty acid soaps. The formation of fatty acid soap is not a bad thing, and the accumulation of soap is the key issue that needs to be solved. For example, under soft water conditions, a small amount of soap is in a dispersed state, which is advantageous and desirable for the cutting fluid to control the foam. In the case of hard water, especially long-term hydration causes a cumulative effect of calcium and magnesium ions, which will form a large amount of soap. The accumulation of fatty acid soap will have a certain negative impact on the cutting fluid and mechanical processing, such as soap will consume cutting fluid. The active ingredient may cause the emulsion to be unstable, resulting in an increase in the consumption of the concentrate. When the soap is in the machine tool or in the centralized liquid supply system, it is bonded with foam, iron powder, miscellaneous oil and the like to form scum. Even when it is a viscous substance, it will bring more problems. They float or accumulate in the working fluid, which not only affects the filtration system, but also causes clogging, increased consumption of filter paper, poor sanitation on the site, and remains in the tool. Machining accuracy issues can arise in gages, fixtures, and drive trains. Quaker Chemical has noticed this phenomenon very early, and conducted a series of in-depth studies on the problem of soap in water-based cutting fluid. This paper introduces Quaker's latest "soap dispersion" technology and successful application in the field. After extensive research, Quaker Chemical's R&D department has discovered a variety of complex “soap-forming†factors, of which water quality, liquid distribution methods, systems, etc. will have an impact on “soapingâ€. In addition, due to the complex formulation of water-based cutting fluids, dozens or even dozens of additives are usually used to satisfy product emulsification, lubrication, corrosion inhibition, microbial control, pH buffering, coupling, defoaming, dispersion and wetting. And other functional requirements. Studies have found that many additives can affect the behavior of soap, such as some polar substances and surfactants can help the solubility of soap in the cutting fluid, part of the soap formed will be dissolved or dispersed in the cutting fluid, and some are insoluble Water will precipitate and collect. Fatty acid is an important additive in the cutting fluid formulation. Its functions include stabilizing the concentrate system, adjusting the HLB value balance and acid-base balance, neutralizing with the amine as an emulsifier and rust inhibitor, and helping the lubrication to a certain extent. It is even more critical for the formation of soap. One of the results of Quaker's research is that different fatty acids have different effects on the tendency to form soap. Quaker's chemistry studies the properties of soaps formed from different structural fatty acids. The selected fatty acids are of analytical grade, including: saturated fatty acids C12, C14, C16, C18 and C22; oleic acid (cis C18-1), erucic acid (cis C22-1), unsaturated Oleic acid (cis C18-2) and trans oleic acid (expressed as C18-T). The test was carried out on a cutting fluid base formulation of Quaker. Different fatty acids were added to the base formula at the same molar concentration. The corresponding cutting fluid was formulated into a 5% dilution with calcium ion-containing water, calcium ions and fatty acids. The molar concentration is calculated to be 1:2, then subjected to the rapid soap test (QSS), and finally the EDTA titration method is used to test the calcium ion concentration in the filtered diluent to obtain dissolved or dispersed in the cutting fluid. In the case of the fatty acid calcium soap, the amount of the fatty acid soap which is not dissolved can be calculated to understand the tendency of different fatty acids to form soap. It can be seen from Fig. 1 that long-chain and saturated fatty acids can form more fatty acid soaps, and most of them are precipitated from the cutting fluid. The soaps formed by unsaturated fatty acids have better dissolution or dispersion properties, and the formation of trans-fatty acids and saturated fatty acids. The properties of soap are similar, similar to C14 saturated fatty acids, and easy to form insoluble soap. This phenomenon is a reminder for the formulation research and industrial production of water-based cutting fluid. The effect of fatty acid composition on soap should be emphasized. For example, industrial oleic acid can be sourced. It is divided into vegetable oleic acid and animal oleic acid, and animal oleic acid has higher content of trans fatty acid. Therefore, in order to achieve effective control of soap in practical application, the chain length and saturation of fatty acid should be reasonably selected, and the source of fatty acid should be controlled. . Gas chromatographic analysis of fatty acid distribution, customer site soap and cutting fluid samples, the data are shown in Table 1. Table 1 Comparison of fatty acid distribution (FAD) in on-site soap and cutting fluid It was found that the on-site soap contained more saturated fatty acids C14, C16, C18, C20 and C22, indicating that these saturated fatty acid soaps were poorly dispersed in water and therefore easily filtered by the filtration system; while the content of unsaturated fatty acids in the soap was Lower than the corresponding fatty acids in the cutting fluid, reflecting the better dispersibility of the soap formed by unsaturated fatty acids in water; the fatty acid data verified the above research rules of Quaker Chemical. The long-chain unsaturated fatty acid erucic acid C22:1 in the on-site soap also precipitated obviously. It is speculated that this is related to the ratio of additives in the water-based cutting fluid formulation and the complexity of the working environment of the on-site cutting fluid. The base oil and synthetic ester in the formula Many factors such as hard water dispersant, surfactant, couplant, etc. will affect the distribution behavior of soap, and the content of calcium and magnesium ions in water, their relationship with fatty acid is also a factor that cannot be ignored, all of which will affect soap. Formation and whereabouts. Quaker's team of experts has undergone a long period of research and experimentation, and created the latest "soap dispersion" technology. From the source of product design, select and strictly control the composition and source of additives such as fatty acids, and comprehensively use soap and base oils, surfactants. The relationship with other polar substances to control the formation characteristics and dispersion properties of soap, effectively avoiding and solving the problem of saponification aggregation in the use of cutting fluid, bringing a good experience and comprehensive performance to customers in the machining industry. Upgrade. Our LED Emergency Twin Spot Lights are a cost effective replacement for old fashioned halogen emergency twin spot fittings. Due to the low power consumption of the LED lamps, only one battery is required, reducing option during charging. The super bright adjustable heads make this twin spot ideal for commercial and industrial applications. with a self test feature every 90 days to ensure correct operation. The Led Emergency Lights design makes it quick and simple to install. Twin Spot Emergency Light,Emergency Twin Spot,Led Twin Spot Emergency Lights,Led Emergency Twin Spot Light Foshan Nai An Lighting Electric Co.,ltd , https://www.articalight.com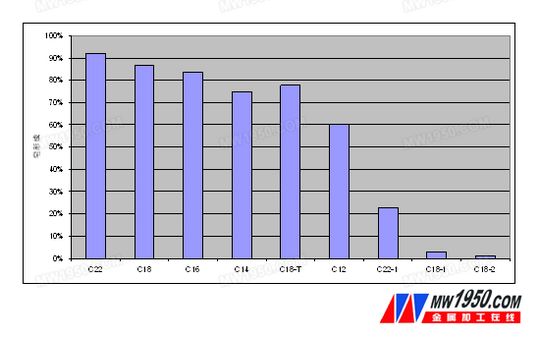
Figure 1 The tendency of different types of fatty acids to form calcium soap 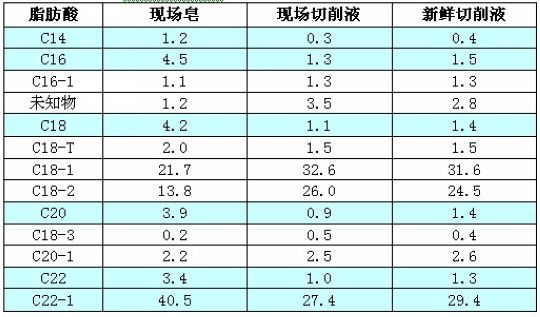
Quaker's latest application of "soap dispersion" technology