Impeller normally applied in the centrifugal pumps.
Impeller is a rotating component equipped in the Pump Housing, help to transfer to energy from the motor that drives
the pump to the fluid being pumped by accelerating the fluid outwards from the
center of rotation.
QFAP supply various kinds of impellers to all over the world, main of our customers are from
Europe, North America, Japan and Southeast of Asia.
Materials:
grey Iron, ductile iron, steel castings, aluminum die castings, etc.
Surface treatment: painting, zinc plating,
passivation, nickel plating, anodizing, polishing, etc.
Heat treatment: according to customer`s
requirement.
QFAP have specialized in producing high
precision Agriculture Parts more
than 10years, Because of the long term cooperation, we could supply our
customers not only the products but also our recommendation on the designs to
saving costs.
Boat Impeller,Fan Impeller,Oil Pump Impeller,Blower Impeller SHAOXING QIFENG AUTO PARTS CO., LTD. , https://www.sxqfap.com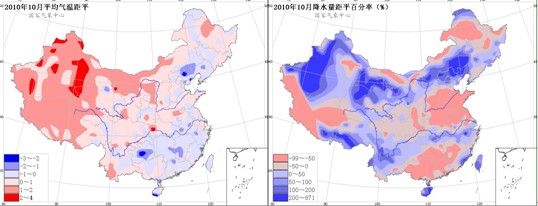

October 2010 Agricultural Meteorology Monthly
This month's summary
The temperature in most parts of the country is normal or high, but the rainfall is unevenly distributed. Most of the autumn harvest area has fine weather and good weather, which is conducive to the mature harvesting of cotton, soybean, rice and other crops and the picking of cotton bolls. Most of the soil in the wheat-seeding area is suitable for soil sowing, which is good for sowing and emergence of winter wheat and seedling growth. Most of the rapeseed in the Yangtze River Basin is planted smoothly and the seedlings are better. However, the rainy weather in the southwestern region has a certain impact on the harvesting progress of autumn harvest crops; it is also not conducive to the sowing and emergence of rapeseed and winter wheat. In Hainan, from late September to mid-October, there was a rare historical precipitation process, which led to serious flooding in the central and eastern regions. Late rice filling and mature harvesting, aquaculture, and rubber, economic forestry and vegetable production were greatly adversely affected. In addition, in the second half of the central and eastern part of the country, there were strong winds and precipitation and precipitation weather processes, which were unfavorable for drying and storage of grain in autumn harvests, slowing the progress of cotton picking, affecting the quality of cotton fiber, and producing a certain amount of facilities for agriculture and rapeseed transplanting in parts of the south. Negative Effects.
Weather and climate characteristics
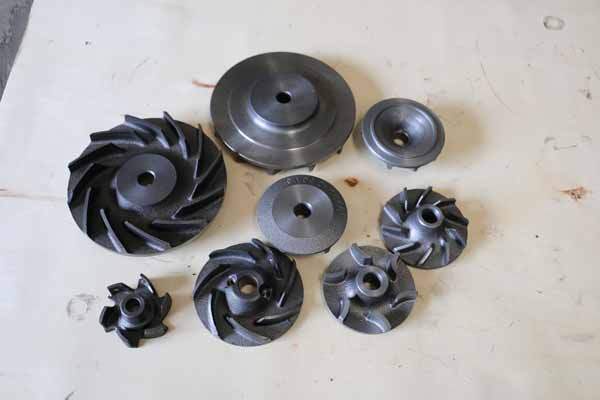
In October, temperatures in most parts of the country were close to normal or high in the same period. Among them, the temperature in the western part of the western region was 1 to 4 °C higher (Fig. 1). Precipitation in the northwestern part of Northeast China, southern part of North China, Huanghuai, northern Jianghuai, southern Jiangnan, and central and western China is less than 50% less than normal. The precipitation in most other parts of the country is close to normal or excessive (Figure 2). In the middle and late mid-term, large-scale winds and precipitation and precipitation weather occurred. In the central Shaanxi, south-central Shanxi, central and southern Hebei, Beijing-Tianjin, southern Shandong, northern Henan, and northern Susong, local frosts appeared on the 26th.
Figure 1 Average temperature anomaly in October 2010 Â Â Â Â Figure 2 October 2010 precipitation amount from
The main agricultural meteorological conditions Agricultural Region of
Northeast: The northern part of the country has less precipitation, higher temperature and sufficient sunshine, which is conducive to the mature harvesting of corn, soybean, and first-season rice. The temperature in the middle and south of the central and southern regions is obviously lower than that of normal years, and the soil in some areas is too wet, which is not conducive to autumn harvest. Crop harvesting and drying, the autumn harvest progress is slow. On the 25th, there was a strong wind and cool rain (snow) weather. The temperature drop in most areas reached 8-12 °C, which was unfavorable for autumn harvesting, autumn harvesting and storage, and greenhouse crop growth.
Northwest, North China, Huanghuai: The temperature in most areas is close to normal or high in the same period of the year. The sunshine is sufficient, and the weather is fine. It is good for mature crops such as corn and soybeans, and cotton boll picking. Most of the soil in the wheat planting area is suitable for winter wheat. The seedlings and seedlings went smoothly, and the wheat seedlings grew well. In northern North China, the temperature is low, precipitation is high, and sunshine is less. It is not good for drying autumn crops, forming strong seedlings for winter wheat, and growing vegetables in greenhouses. The strong cold air process in the latter half caused the temperature drop in North China and Huanghuai to reach 6-12 °C, which was unfavorable for the drying and storage of grain in autumn, which also slowed the progress of cotton picking and affected the quality of cotton fiber.
Jianghuai and Jianghan: The temperature in most areas is close to normal, the precipitation is slightly less normal, and the light is more abundant, which is conducive to rice maturity ripening, harvesting and drying, and cotton cracking bolls and picking; winter wheat sowing and seedling, rapeseed planting smoothly, and seedlings are better. However, the precipitation in some areas of northern Jianghuai continued to be less, and there were different degrees of drought. The emergence of wheat after planting was difficult, and the transplanting of rapeseed was also affected.
Jiangnan: Most of the southern part of the country is dominated by sunny to cloudy weather, which is conducive to maturity and harvesting of late rice. There is a lot of precipitation in the northern region, which has an adverse effect on late rice filling and mature harvesting, cotton boll picking and rapeseed sowing. The eastern part of the southeastern Yangtze River is affected by the No. 13 typhoon "squid", which has a strong precipitation process and matures in late rice. Sun exposure has a certain impact.
South China: Temperatures in most areas are close to normal or slightly lower, with less precipitation and sufficient sunshine, which is conducive to late rice heading, grain filling and ripening. There were two periods of heavy precipitation in late Hainan from mid-September to mid-October, and severe flooding occurred in the central and eastern regions. Late rice grain filling, mature harvesting, and rubber, economic forest fruit and vegetable production suffered large losses. In the latter half of the typhoon "Squid" landing in Fujian, agricultural production in parts of eastern China was greatly affected.
Southwest: Most of the monthly precipitation is more than 30% to 1 times. The light is obviously insufficient. The farmland soil is too wet, which is not conducive to the harvesting and storage of autumn harvest crops. It is also not conducive to rapeseed and winter wheat sowing.
The main agricultural meteorological disasters
Heavy rains and floods: Hainan and southwestern Guangdong suffered heavy rains and floods during the month. Among them, there was a history of persistent heavy rainstorms in the first half of Hainan. In some areas, there were serious floods, grain filling in late rice, mature harvesting, rubber tapping, and tropical fruits. And vegetable production and aquaculture have a greater impact, causing 102.6 thousand hectares of crops in Hainan to be affected, including 27.1 thousand hectares; Guangdong's crops affected by 13.0 thousand hectares. Heavy rains in the middle caused 99.6 thousand hectares of crops in Hainan to be affected.
Snowstorm: From October 23 to 28, parts of five cities including Wuwei, Jiayuguan and Jiuquan in Hexi area of ​​Gansu Province suffered from low-temperature freezing and snow disasters, and the affected area of ​​crops was 3.2 thousand hectares. The largest snowfall center is located in Wuwei City, with a depth of 14-15 cm. The snow has caused many trees in the Hexi area of ​​Gansu to collapse, and the facilities agriculture is seriously affected. The solar greenhouse, the greenhouse and the ring shed are damaged to varying degrees (Figure 3).
Typhoon: In the early period, it was affected by Typhoon No. 13 "Squid". In the southeastern coastal areas, there were strong storms and rains, and agricultural production in the eastern part of the Yangtze River and parts of eastern China suffered heavy losses. According to statistics, as of October 25, the area affected by crops in Fujian was 36.1 thousand hectares, and the area affected by crops in Guangdong was 2.3 thousand hectares.
Drought: The precipitation in Anhui and parts of northern Jiangsu has been less than 50 mm since mid-September. The soil moisture in farmland has continued to decline, and there are different degrees of drought, which is unfavorable for winter wheat sowing and seedling growth.
Cold dew wind: A slight cold dew wind appeared in the southern part of Hunan, northwestern Jiangxi, and northwestern Guangxi, which had some adverse effects on the late rice that was still in the heading and flowering stage and the early stage of fruiting.
Chilling damage: In the second half of the year, affected by the strong cold air in the north, most of Guangxi experienced obvious cooling weather. The cold damage caused the early leaf senescence of late rice, the photosynthesis ability decreased, and the grouting was inhibited, which affected the yield increase.
Hail: In the southern part of Gansu Province, the area affected by the gale and hail disasters was 1,000 hectares. On October 19, Dingxi County, Gansu Province, suffered from wind and flood disasters, with an area affected by crops of 56 hectares; a windstorm occurred in Xiji County, Guyuan City, Ningxia, with an area affected by crops of 3.6 thousand hectares.
Weather conditions and agricultural prospects recommend
It is expected that in November, most of the country will have less precipitation, which is conducive to the harvesting and storage of late rice in the south. However, the precipitation in the northern part of Jiangsu and northern Anhui is less than 2 to 50%, which will make the drought continue or develop, which is unfavorable for winter wheat growth. Precipitation in most of the Northeast, northeastern Inner Mongolia, northeastern Xinjiang, south China coast, southwestern west, and eastern Tibet will be more than normal. Snowstorms may occur in some areas, which will have certain adverse effects on agricultural production in the above areas.
It is expected that in November, there will be four cold air processes affecting China, and the cold air force will be further enhanced. The staged low temperature is not good for the growth of winter wheat and rapeseed. To this end:
1. In the northern winter wheat area, it is necessary to strengthen the field management. After the wheat emerges, it is necessary to check the seedlings in time to ensure that the wheat seedlings are fully seeded, and pay attention to watering and fertilizing at the right time, so as to promote the cultivation of the wheat seedlings and promote the formation of strong wheat before winter. seedling. The areas with severe drought in the northern part of the Yangtze River and Huaihe River should be timely watered to prevent the late development of drought and affect the growth of wheat seedlings.
2. The rapeseed production area in the Yangtze River Basin should strengthen the field management, pay attention to the seedlings and replant the seedlings, and pay attention to the timely fertilization of the transplanted rapeseed. The areas with different grievances should be timely irrigated to improve the soil moisture and improve the survival rate of rapeseed transplanting.
3, Jiangnan and South China must seize the fine weather, timely harvest mature late rice.
4. The area where the soil in the southwestern soil is too wet should pay attention to clearing the ditch, draining the water and reducing the waterlogging, ensuring the smooth transplanting of winter wheat sowing and rapeseed.
5. The northeastern part of Xinjiang and the northeastern part of Inner Mongolia have more precipitation in November, and the agriculture and animal husbandry should pay attention to the prevention of snowstorms.
Total 1 | <First <Prev 1 Next> Last> |
share to: