I. Introduction January 2017, Tenth International Workshop on Fire instructor in Hong Kong, set mob family, exchange new ideas. One of the reports elaborated on the "strategic-tactical-technical" model mentioned by the author. John McDonough from Australia talks about several tactical choices that must be made on the fire. Although he agrees that today's firefighting operations can jump out of the way of thinking, but also pointed out that each inward attack, there are several things that must be done: he called it "the five criteria" - that must be implemented. Second, the attack In the past fifteen years, the concept of fire fighting has undergone tremendous changes. During this period, people who joined the fire service learned a lot of relevant knowledge during basic training. But for the older comrades, it is another matter. The methods and methods are constantly changing and the pace of change is never stopped. In addition to extinguishing fires, fire fighters must also have knowledge of the areas of vehicle rescue, hazardous chemicals disposal, and traffic safety, so it is understandable that some people will not see Taishan because of a blind vision. Therefore, fire-fighting training schools and instructors are required to highlight the key points when explaining problems. Schools must have enough vision in these areas. Even if they know that the realization of the new idea cannot be accomplished overnight, it should be disseminated. Some new developments will provide a little help in extinguishing the fire and make things simple; while others are truly decisive improvements - making extinguishing more safe and effective. There are frequent fires in buildings with small fire compartments such as houses, apartments, hotels, nursing homes, small office buildings, etc. Therefore, there are usually fixed models for fighting against these types of fires. On the contrary, there are no fixed procedures for fighting fires in large stadiums, movie theaters, and industrial buildings. At this time, the commanders' need to adapt. Even in normal circumstances, some things are not flexible. Firefighters who perform internal fire extinguishing in buildings such as houses and office buildings should always be able to do the following five things: " 1 " stays low " 2 " controls the flow of smoke " 3 " cooling flue gas " 4 " shoots water to the fire as soon as possible " 5 " uses a thermal imager Third, the five principles of fire fighting within the attack 3.1 Staying low In the past, firefighters were taught to stand on the fire. After all, what is used in personal protective equipment training courses is standing and walking. This method is jokingly called overseas "dance to dance" or "fire kung fu." There are many disadvantages to standing in a smoke-filled room, so it's best to keep it low: Always have at least one knee on the ground at all times. Figure 1 Argument to stay low in infighting At the beginning of the internal attack training, the first thing that was introduced was the transition from the standing position to the low position in the fire. As we all know, the temperature in the hot smoke layer is higher than that under the smoke layer. Therefore, it is not necessary to change the temperature of the smoke layer.å´´ æ┩ å´´ å´´ å´´ 虢ㄖ 然 然 然 然 然 然 å…± å…± å…± å…± ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? è°˜ è°˜ è°˜ ç‹» ç‹» ç‹» They ignore the fact that when you feel too hot and have to adopt a low attitude, can you continue to attack? At this time, the heat absorbed by their battle suits is much higher than that of firefighters who started to take a low position. Second, taking a low profile in the offense is a better view. The temperature below the smoke layer is lower than the top and the field of vision is better below. Even if the entire room is filled with smoke, the line of sight near the ground is slightly better. And because the smoke is slightly thinner there, using hand electric energy to see further away, it is easier to find the fire point. More importantly, the layout of the room can be inferred from the information observed near the ground: Where is the furniture? How to make the water belt extend forward? It is not easy to infer this information when you are standing. Third, on the floor or near point is also the easiest place to find the wounded (for example, on the bed or sofa), the wounded are rarely to be found in places off the ground more than 1.5 meters high. If the search and rescue team is standing for search and rescue, the height of the light search is wrong, and the height of the search and rescue group with a low attitude is just right: it is more effective near the ground because it is easy to reach the sofa and bed. In addition, the lower position is easier to search under the furniture (such as a table) and the standing position is not so easy. When the situation is low, it is very unlikely that the search and rescue team will ignore the wounded people next to the route. Of course, the right search and rescue method must be adopted. Extending the leg forward to make a fan-shaped sweep can quickly and easily find the wounded in a large area. Fourth, the thermal imager also has a blind spot when it is used. Things near the firefighter in front of the ground cannot be displayed on the screen, and the higher the instrument is lifted, the larger the blind spot. Fifth, when you stand and walk, the two legs are used for "support" and "perception". To avoid falling, use the sensing leg to explore the front ground before moving the support leg. If you take a low position, the firefighter's center of gravity is lower and closer to the ground. You can avoid losing balance by stepping on the foot and falling down stairs or holes. In Belgium, firefighters rarely fall into holes or collapse floors. However, the popularity of light-weight structures (introduced later in the orange rescue public number) increases such risks. When standing, people only have two contact points with the ground: both feet. Therefore, the firefighter taking a low position should be much more stable, because he or she usually has a lower part of a leg and a foot in contact with the ground. Water gunners must counteract several counter-forces when they are advancing. In the case of zero visibility, the low profile march is definitely easier than standing. And if the firefighter is close to the ground, the consequences will not be very serious if he loses the balance. He (she) can maintain balance by rolling on the ground or by hand. But if you lose balance and fall while standing, the firefighters will throw straight to the ground - and this is exactly what is to be avoided in the fire. 3.2 Control of smoke flow trajectory In the past few years, people gradually paid more attention to controlling the flow of smoke on fire. Compared to Belgium, North America places more emphasis on this matter. After all, horizontal exhausting by breaking windows is already a routine action. In fuel-controlled fires, this can be done without increasing the fire. In the past, most of the fire brigades faced when they arrived were fuel-controlled fires. The development of such fires was relatively slow. Now the fire is developing very fast. If the oxygen is sufficient, a flashover will occur within 2 to 4 minutes. However, in most cases it is not possible to have enough air. In a closed house, the combustion will be turned into ventilation control before the flash fire. This is called a ventilation-controlled fire. In a fire with almost no oxygen, if the window is suddenly broken or broken, the temperature of the fire field will rise sharply and (by ventilation) flash fire. Figure 2 Different causes of the smoke trajectories controlled by firefighters In Europe, firefighters rarely intentionally break the windows for ventilation, because opening the door is equivalent to venting, and the door is one of the passageways through which air flows into the interior of the building. In today's fire fighting, it is very important to control the flow path of smoke. One person can be kept by the door (gating). The person's task is to close the door as small as possible, while conveying the hose inside the building and ensuring that the hose is not worn by the door. If the door is the only opening, the person at the door also controls the intensity of the fire. Assuming that a door is 90cm wide and fully open, the burning is ten times more intense than when only artificially opened 9cm - a tenfold larger opening means ten times the amount of air flowing in, which means ten times more violent burning . In Belgium, the concept of gate control is still very basic. Normally, firefighters are a group of two when performing a task, and two teams of players on the tanker perform internal attack and water supply, respectively. In fact, this method is outdated. Most of the time, the first group is to carry out internal attacks, but the other group should be redistributed according to the situation on the spot. In today's firefighting and rescue operations, fire engines arrive from different fire brigades, and the tanker commander can choose to have the entire tanker combat class (two groups) responsible for offensive lines. He could disassemble the second group, arrange three firefighters to drag off the attacking water, and the fourth to control the smoke flow at the door. A tanker commander can also drag a hose behind the offensive team, so that the deployment is faster and the hose attack is also faster. Just because of the rapid development of today's fire, this method is also very effective. However, the tanker commander must keep communication with the driver at all times, and he needs to be in contact before the command vehicle or other tanker arrives. There is another way to control the flow of smoke: German fire officer Michael Reick invented the “smoke blocker†for this purpose. This simple device is hung on the door with a fireproof cloth similar to a fire blanket and can be operated by only one player. If you open the door, you can complete the deployment before you open the door. Trained firefighters can even rely on tactile sensations to deploy in smoke-filled rooms. The “smoke blocker†completely blocks the flow of hot smoke and protects adjacent rooms from being affected. It is even more efficient than the “gatekeeperâ€, because shutting down the door will make the smoke flow in. In addition to the prevention of smoke outflow, “smoke blocker†can also prevent large amounts of air from entering. Only a small amount of air can flow into the door gap near the ground. The Antwerp Fire Department in Belgium has been unconventional. The "smoke blocker" has been equipped with water tankers. The Brussels Fire Department has also begun to use. There is no doubt that this equipment will have more users in the near future. In a unit fire, the tanker commander can conveniently arrange two groups of personnel: the second group installs a “smoke blocker†at the door of the unit, and when a group begins to extinguish, the second group can search and rescue. Another benefit of controlling the flow trajectory is that it limits the rate of smoke spread within the building. In ventilated controlled fires, the smoke layer is often close to the ground. Fire fighters must work in the smoke layer and heat is transferred from the smoke layer to the firefighters. After the combat suit has absorbed a certain amount of heat, the firemen must be forced to leave the fire in order to avoid burns. The higher the flue gas temperature, the faster the heat transfer rate. Moreover, the speed of the flue gas flow will increase the speed of heat transfer. Therefore, controlling the flow rate of smoke can provide great help for in-flight personnel. Whenever, controlling the smoke flow trajectory means one of the correct door-to-door processes. Fortunately, Belgium has already promoted this process as a well-known action method. Although there is still room for improvement in the standard entry procedures that are officially promulgated, they have also made great progress. Opening the demolition technique to lock the door - it also needs more attention. When a door is forced open, smoke trajectories should be considered. This can be solved by attaching a strap to the door handle. Without the lock, the firefighter can still control the size of the door switch and use it to control the amount of gas flow. Of course, the door can be completely closed before the “smoke blocker†is deployed. 3.3 Cooling smoke As early as 2000 , Belgian firefighting introduced the concept of flue gas cooling when introducing “ 3D fire extinguishing technologyâ€. Slowly everyone knows that the internal attack team should pay attention to the cooling of the smoke during the attack. The question is not "whether or not to cool the flue gas" but "to what extent does the flue gas be cooled?" What are the consequences of cooling the flue gas when it is not necessary? The water will flow back to the ground and there will be water droplets on the walls and ceiling. Due to the smoke, the room must be repainted anyway. Therefore, there is no harm in unwanted flue gas cooling. But what if there really is a need to cool the flue gas without cooling it? In some cases, the smoke layer will flare up, which will cause the room to go off and the in-house attackers will sacrifice it. Therefore, no cooling of the flue gas when cooling is required will have serious consequences. Figure 5 cooling smoke is very important It is important to pay enough attention to the cooling of smoke. In actual combat, flowering shoots are most effective: the flowering angle is set to 30 to 40 °, and the water gun is turned on for 2 to 3 seconds each time . Refer to the “Water Spray Point Theoryâ€. According to the location of the smoke that needs to be cooled, the water gun can be directed upwards or diagonally upwards. There must be a clear understanding of how far the water droplets can be played in the firefighter's head, which determines the extent to which it can be cooled. The flow of the water gun does not need to be too high, and a flow of 200 liters / minute is sufficient. It is important to have high-quality water guns that can produce suitable water droplets and ensure the water pressure of the water flow. Modern water guns require at least 6 to 7 bar water pressure. If you're wearing a jacket, you're not going to know what you're doing. As its name implies, it is to reduce cooling the flue gas flue gas temperature, since the heat emitted low smoke fewer layers (either by convection or thermal radiation), but also the internal environment safer: 1, slow flashover; 2, The steam generated by the water droplets is mixed with the flammable flue gas to reduce its flammability and reduce the possibility of rotting. Normally, the smoke layer will smash outwards from the fire point. However, after the flue gas began to cool, the flue gas flow was briefly stopped. As the speed of its spread decreased, the amount of heat emitted by the heat convection decreased accordingly. As the temperature of the smoke layer decreases, its volume decreases accordingly, and the reduced volume is compensated by the converted water vapor. In view of this, the flow of the water gun should not be too large. Excessive flow rate will generate a large amount of water vapor, and in the case of the same room volume, turbulence will form at the ceiling and cause the phenomenon of reverse temperature - water vapor will have high temperature smoke pressure. To the ground, affecting firefighters. Finally, information on the temperature of the smoke layer can be obtained by cooling the flue gas. If you hear a "click", it means the water evaporates in the smoke. The size of the sound shows the temperature of the smoke on your head. Therefore, cooling the smoke is also a way to check the temperature of the fire. 3.4 Fire the water as soon as possible In most parts of the world, fire extinguishing has long been the standard method of action. The use of air calls made it possible to search into rooms full of smoke and extinguish fires. Figure 7 There are many ways to extinguish a fire. The faster you do it, the better. Everyone agrees that the internal attack is more advanced than the previous old method (dumping water from the outside until the fire is extinguished). In the past, sometimes several tons of water were thrown into the windows, and the water loss was even greater than the damage caused by the fire. About 40 years ago, the fire was transferred from the outer attack to the inner attack. The outer attack was almost forgotten. In most countries, it is generally believed that professional firefighters attack internally and amateurs attack outside. However, studies in the United States have shown that it is possible to combine the two: If the offensive can directly hit the fire, it is better to attack the fire first to reduce the heat release rate. In the United States, this method has a different name: external strikes, weakening the target. Upon arrival, the firefighters first attempted to suppress the fire externally, followed by an internal attack. This tactic was a "transitional attack." 3.5 Using Thermal Imager Over the past decade, thermal imagers have become standard for firefighters. Every tanker now has at least one thermal imager. Of course, you should use it instead of eating it in the car. The in-game team should carry a thermal imager that can be used to locate trapped people, in addition to locating fire spots. In addition, the thermal imager can also assist in evaluating the effectiveness of the water gun, ie cooling the smoke and extinguishing the fire. In terms of these two points, the thermal imager is a valuable asset (some of the domestic thermal imagers are not real imagers). Fourth, the prerequisite For many fire control agencies, implementing the "five criteria" is not a simple matter and requires a lot of energy. There are several prerequisites for fire fighters to practice the five criteria: First, firefighter training. If the superior requires the grass-roots to complete the task brilliantly, it must provide professional education and training. Which should include: theory, simulation training and real fire training. It is important for firefighters to understand their working environment. In addition, they must first simulate training and then train in different types of skills in real fire conditions. Only in this way can our group (instructors) expect firefighters to perform their tasks well on the fire. Second, we must formulate rules and regulations for the "five criteria." Here's a simple example: If you face a fiery burning fire, have a well-ventilated opening, and the opening is easy to reach, a transitional attack is the standard procedure. Third, the five points in the "five criteria" need to be incorporated into the standard action guides commonly used in firefighting. The Standard Action Guidelines stipulate how all personnel should act after they arrive. It is important that the combatants, water tanker commanders, and field commanders follow the same procedure. Fourth, a very important responsibility that commanders at all levels must undertake is to ensure that firefighters adopt established methods on the fire. Everyone knows what to do when training, but on the fire, the commander needs to spend enough time and energy to ensure this. All commanders must play a leading role in attitude and professionalism at the same time. This article comes from Micro Signal Orange Rescue.
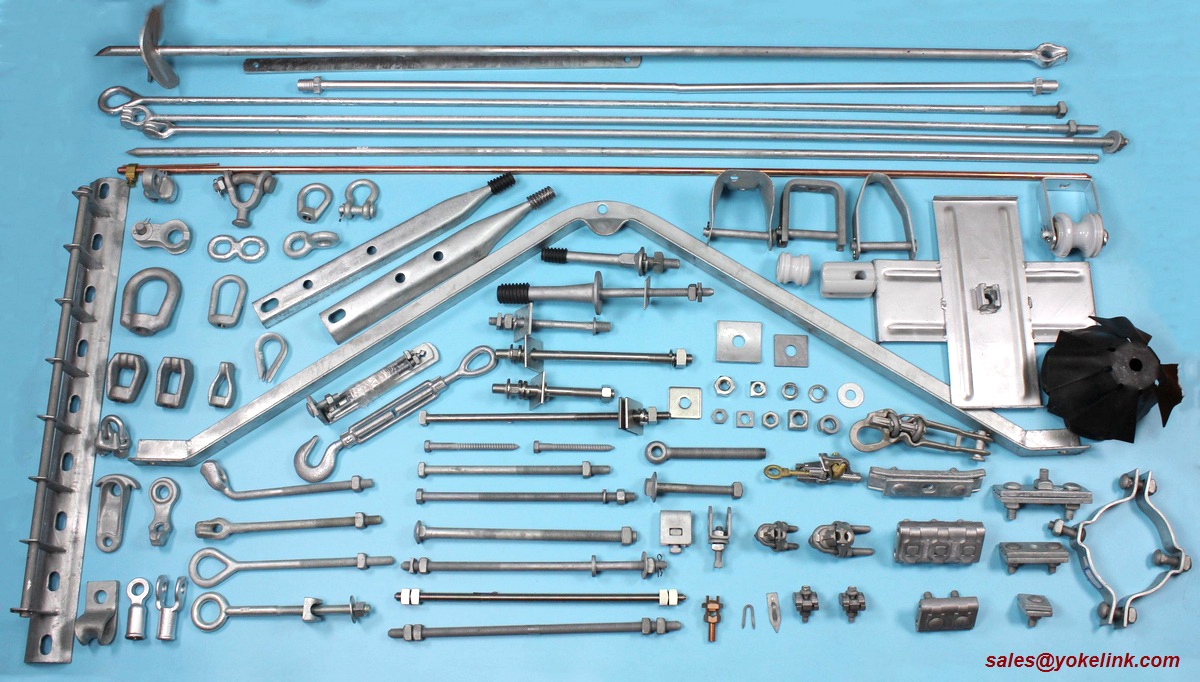
Pole line hardware refers to a range of products and accessories used in the construction and maintenance of overhead power lines. It includes various components such as pole brackets, crossarms, insulators, guy wires, and clamps that are essential for supporting and securing the electrical cables to utility poles. These hardware items are designed to withstand the weight and tension of the power lines, ensuring their safe and reliable operation.
Yokelink supply a full line of Poleline Hardware, we offer from the top of the pole to underground. Here are some of the pole line accessories that you are likely to use for your project:
Pole Bands
Guy Clamps
Also known as a dead-end grip, this pole line hardware is usually used on the distributed cables. It is usually attached to the grip conductor and as well as for the optical fiber.A guy grip has helical which is capable of holding the cable.
Guy Thimble
Also known as cable thimble, this utility pole accessory is usually used in conjunction with guy grip. The thimble acts as an interface between the pole band and the guy grip.
A secondary clevis comprises of a punched steel and a clevis pin. It is also known as dead-end clevis and is characterized by the D-shaped bracket. The main function of this powerline accessory is to connect with the pool insulator to the pole.Apart from the overhead line, this accessory is also used on the dead end.
Secondary Rack
As overhead line hardware, a secondary rack works as a platform for holding insulators. The u-shape design of the rack allows it to support the maximum number of insulators at any given time. It all depends on the number of spools that are on the rackThe smooth edges of the rack do not scratch he attached insulators on the rack.
Power line hardware, Utility pole hardware, Electrical pole hardware, Pole line construction hardware Ningbo Yokelink Machinery Co.,Limited , https://www.yokelink.com






POLELINE HARDWARES
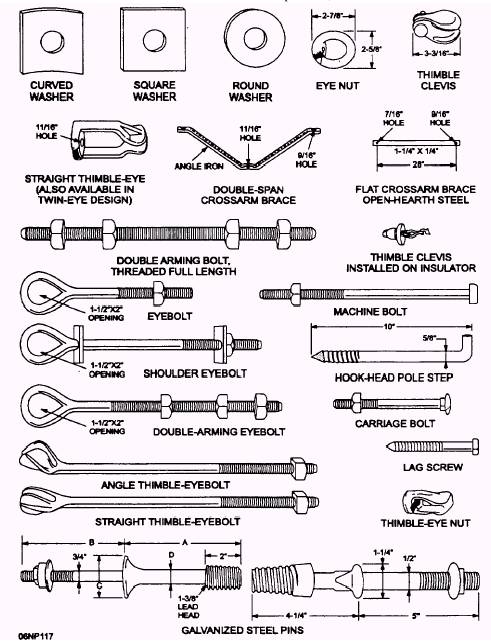
A pole band is used as a point or platform for creating secondary racks to the pole. It is sometimes referred t as a fastening clamp or simply a pole fastener.
Guy Wire
Also known as a stay wire, this hardware is usually used for enhancing the stability of the pole. It balances the load that is on the electric pole.
Stay wire is usually assembled with other accessories such as pole bracket, guy thimble, and stay rod so that it can attach to the pole and ground.Guy wires must have high tensional strength to sustain the forces against it.
Anchor Rods
You will have to buy guy anchor whenever your project entails attaching guy wires onto the power line. The anchor plays the role of connecting the guy wire to the ground.A guy anchor should be strong and have adequate tensile strength to support the force of the wire.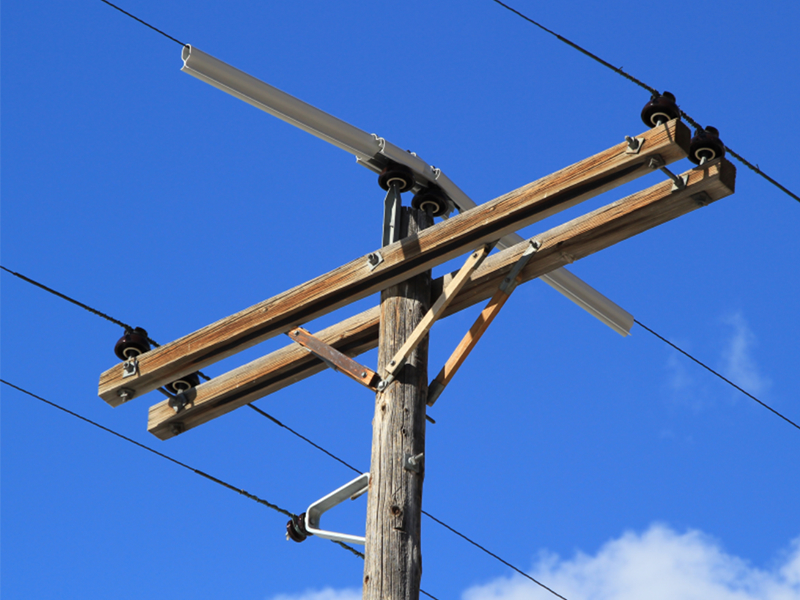
You will need the best guy clamp to secure the strands of guy wire. The clamp comprises two pieces of carbon steel that are designed to form a parallel groove.The design of the clamp ensures that there is minimum damage caused on the strands of the guy wires.
Guy Grip
It can also connect to the tension clamp in order to protect the ADSS cable. You can also use the guy thimble to connect the stay rod to the guy wire.
Insulator Clevis

Crossarm Braces & Bracket
This utility pole hardware is literally the arm of a streetlight pole. It extends from the pole to provide a platform where you will attach the lighting fixtures.Streetlight arms come in different lengths and designs depending on the needs of the users.
Crossarm Braces & Bracket
This utility pole hardware is literally the arm of a streetlight pole. It extends from the pole to provide a platform where you will attach the lighting fixtures.Streetlight arms come in different lengths and designs depending on the needs of the users.
"Fire Fighting Technology" firefighters attack fire fighting rescue technology
News Related Keywords: No tags.