introduction The pulse tester is an electronic device used to measure the number of pulse beats in a person. It is also a major component of the electrocardiogram and therefore plays an important role in modern medicine. Although there are many instruments for detecting pulse, there are few portable all-digital pulse measuring devices that can perform various functions such as accurate measurement, accurate display, and accurate timing function. With the improvement of people's living environment and economic conditions, as well as the improvement of cultural quality, their lifestyle, health care needs, disease types, and treatment measures have undergone significant changes. However, at present, China's cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases are still rising year by year. Its morbidity and mortality rank first among various diseases and is one of the main causes of human death. Therefore, it is necessary to recognize, prevent and detect these diseases early. The extraction of physiological and pathological information of human body from pulse wave as the basis of clinical diagnosis and treatment has always been valued by Chinese and foreign medical circles. Almost all the people in the world have used the “touching pulse†as a means of diagnosing diseases. The comprehensive information of the shape (waveform), intensity (amplitude), velocity (wave velocity) and rhythm (cycle) exhibited by the pulse wave largely reflects the blood flow characteristics of many physiological and pathological processes in the human cardiovascular system. Therefore, it has high medical value and application prospect for pulse wave acquisition and processing. However, the biological signals of the human body mostly belong to the low-frequency weak signal in the background of strong noise, and the pulse wave signal is a non-electrophysiological signal with weak low frequency, which must be amplified and filtered to meet the requirements of the acquisition. 1 basic structure module 1.1 pulse wave detection circuit At present, the pulse wave detection system has the following detection methods: photoelectric volume pulse wave method, liquid coupled cavity pulse sensor, piezoresistive pulse sensor and strain gauge pulse sensor. In recent years, photodetection technology has developed rapidly in clinical medical applications. This is mainly due to the fact that light energy avoids strong electromagnetic interference, has high insulation, and can detect various symptom information of patients non-invasively. The use of photoelectric method to extract fingertip pulse light information has been valued by experts and scholars working in biomedical instruments. The system is designed with a finger-type transmissive photoelectric sensor, which realizes photoelectric isolation and reduces interference to the analog circuits of the latter stage. A sensor is a measuring device that converts a measured value into a certain physical quantity that is suitable for application with a certain degree of precision. The photoelectric sensor used is composed of a light-emitting diode and a photodiode. The working principle is that the light emitted by the light-emitting diode is transmitted through the finger, and the blood absorbed and attenuated by the finger tissue is received by the photodiode. Since the finger arterial blood has a periodic pulsating change during blood circulation, its absorption and attenuation of light is also periodically pulsating, so that the change of the photodiode output signal reflects the pulsation of the arterial blood. 1.2 pulse signal pickup circuit The infrared receiving diode can generate electric energy under the illumination of infrared light, and a single diode can generate 0.4_V voltage and 0.5mA current. The BPW83 infrared receiving diode and the IR333 infrared emitting diode have a working wavelength of 940 nm. In the finger clip, the infrared receiving diode and the infrared emitting diode are placed opposite each other to obtain the best directivity. The larger the current in the infrared emitting diode, the smaller the emission angle, and the greater the intensity of the emission. In Figure 1, R0 selects 100 Ω based on the sensitivity of the infrared receiving diode to sense infrared light. R0 is too large, the current through the infrared emitting diode is too small, and the PBW83 infrared receiving diode cannot distinguish between the pulse and the pulseless signal. On the contrary, if R0 is too small, the current passing through is too large, and the infrared receiving diode cannot accurately distinguish the signal with and without pulse. When the infrared light emitted by the infrared emitting diode is directly irradiated onto the infrared receiving diode, the potential of the inverting input terminal of IC1B is greater than the potential of the non-inverting input terminal, and Vi is “0â€. When the finger is in the measurement position, two situations will occur: one is the pulse-free period, although the finger blocks the infrared light emitted by the infrared emitting diode, but due to the dark current in the infrared receiving diode, there is still a dark current of 1 μA. The Vi potential is slightly lower than 2.5V. Second, there is a pulse period. When there is a beating pulse, the blood pulse makes the finger translucency worse, the dark current in the infrared receiving diode decreases, and the Vi potential rises. 1.3 Signal Acquisition and Processing System Because the photoelectric pulse wave belongs to a slowly changing weak physiological signal, the signal-to-noise ratio is low, and it is highly susceptible to interference from environmental noise and limb movement. The traditional photoelectric pulse wave signal detection circuit uses a high gain amplifier to obtain high detection sensitivity. This design idea leads to a reduction in the dynamic range of the detection signal, which will result in photoelectricity due to interference signals when subjected to motion interference. Saturation distortion detected by pulse wave signals. The system uses oversampling technology to improve the sampling accuracy by high-speed sampling of the signal, which is equivalent to analog-to-digital conversion of the signal with a high-resolution ADC, thereby achieving the effect of improving the signal-to-noise ratio and improving the dynamic range. Therefore, the system performs analog-to-digital conversion on the photoelectrically converted signal without any signal conditioning (amplification and filtering) circuitry. 1.4 Application of oversampling technology The so-called oversampling technique refers to a method of sampling an analog signal at a frequency much higher than the Nyquist sampling frequency. According to the signal sampling quantization theory, if the minimum amplitude of the input signal is larger than the quantization level of the quantizer, and the amplitude of the input signal is randomly distributed, the total power of the quantization noise is a constant, and is uniformly distributed in the frequency range of 0 to fs. Therefore, the quantization noise level is inversely proportional to the sampling frequency. If the sampling frequency is increased, the quantization noise level can be lowered, and since the baseband is fixed, the noise power in the baseband range is reduced, and the signal-to-noise ratio is improved. Increasing the resolution, and increasing the sampling frequency by 4 times, the signal-to-noise ratio is increased by 4 times, which is equivalent to an increase of 1 bit in A/D resolution. 80G Fm Radar Level Meter,80G Liquid Level Sensor,Level Monitoring Gauge,Anti-Corrosion High Precision Radar Level Gauge Jiangsu Pinpai Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.jspingpa.com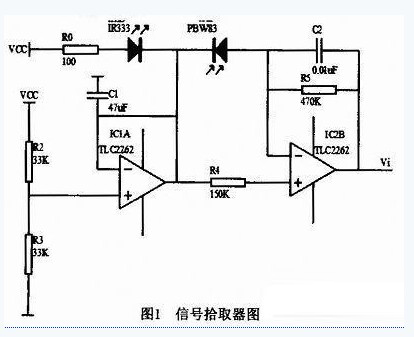
Design of pulse measuring instrument based on single chip technology