With the acceleration of industrialization and the advancement of agricultural industrialization, China has become the world’s largest producer and consumer of reactive nitrogen and organic compounds. The large amount of nitrogen fertilizer application has also brought about negative impacts in ensuring food production. Agricultural non-point source pollution is serious; organic compounds can cause irreversible and serious damage to human health, and have become the focus of pollution prevention and control. In April 2015, the State Council promulgated the “Water Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan†(“Water Ten Articlesâ€), which explicitly requires the implementation of comprehensive prevention and control of agricultural non-point source pollution and the evaluation of organic pollution risk. In response to groundwater nitrate pollution in agricultural non-point source pollution and pollution of organic compounds in water, Han Dongmei, a researcher at the Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and its collaborator system collect data from nationwide surveys on the groundwater nitrate pollution and water bodies in China. Organic pollution has been fully analyzed and evaluated. The researchers integrated and analyzed the deep and shallow groundwater nitrate survey data of 52 basin-scale groundwater systems across the country, and conducted a comprehensive assessment of groundwater nitrate pollution. The results show that of the 36 major shallow aquifers in the major basins, 90% of the monitoring sites in the 25 basins exceed the drinking water quality standards in China (10 mg/LN in terms of nitrogen); in the deep or karst aquifers of 37 major basins, Ten basin aquifers exceeded the standard. The degree of nitrate pollution in groundwater in coastal areas, especially in coastal karst areas, is much higher than in inland areas. Nitrogen isotope traces show that, in addition to agricultural fertilization, nitrogen and domestic wastewater discharges are also important factors affecting nitrate distribution in groundwater. There is a deep-seated trend of nitrate pollution, which is related to the penetration of deep and shallow aquifers caused by massive agricultural irrigation machine wells and scrapped wells. In order to prevent further contamination of deep groundwater, it is imperative to carry out the investigation of the scrapping wells and effectively seal wells. The study selected typical persistent organic pollutants (POPs) and comprehensively analyzed their distribution in different water bodies (including river water, reservoirs, lake water, groundwater, and coastal seawater). The results show that the economically developed Yangtze River Delta, Pearl River Delta, Minjiang Delta, and Zhejiang Province are the hardest-hit areas for POPs pollution. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are found in surface waters in these areas. The concentration of both exceeded the international and Chinese water quality standards. The pollution level of OCPs in China's aquatic environment is comparable to the world's representative area, but the pollution degree of PAHs and PCBs is extremely serious (PAHs regional average is 15.1-72400 ng/L; PCBs regional average is 0.2-985.2 ng/L). PFOS and PFAA contamination have begun to appear. The study used a series of methods such as diagnostic proportions of compounds to analyze the main sources and migration processes of POPs, proposed the schematic diagram of the process of migration and transformation of major organic pollutants in the hydrosphere, and considered that the large-scale hydrological cycle is an important control condition for controlling pollutant migration. . Both studies have shown that groundwater pollution in coastal areas is much higher than in inland areas, and may cause deterioration of coastal water quality and affect marine ecology. Seawater intrusion and groundwater pollution caused by overexploitation of groundwater in the coastal area are intertwined, resulting in an extremely complex coastal environment protection and pollution remediation. The control and rehabilitation of water pollution still needs continuous efforts, and the research has put forward a series of specific countermeasures. The above research was funded by the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the National Natural Science Foundation of China. An electric Globe Valve is a type of valve that is used to regulate the flow of fluids in a system. It is operated by an electric motor or actuator that opens or closes the valve to control the flow of the fluid. The valve has a globe-shaped body with an inlet and an outlet, and a movable disc or plug that is connected to the actuator. When the actuator is energized, the disc or plug moves away from the seat, allowing the fluid to flow through the valve. When the actuator is de-energized, the disc or plug returns to the seat, stopping the flow of the fluid. Electric globe valves are commonly used in HVAC systems, water treatment plants, and industrial processes where precise control of fluid flow is required. Electric Gate Valve,Electric Actuated Gate Valve,Electric Actuator For Gate,Motorised Gate Valve WUXI KVC-VALVE , https://www.kvgatevalve.com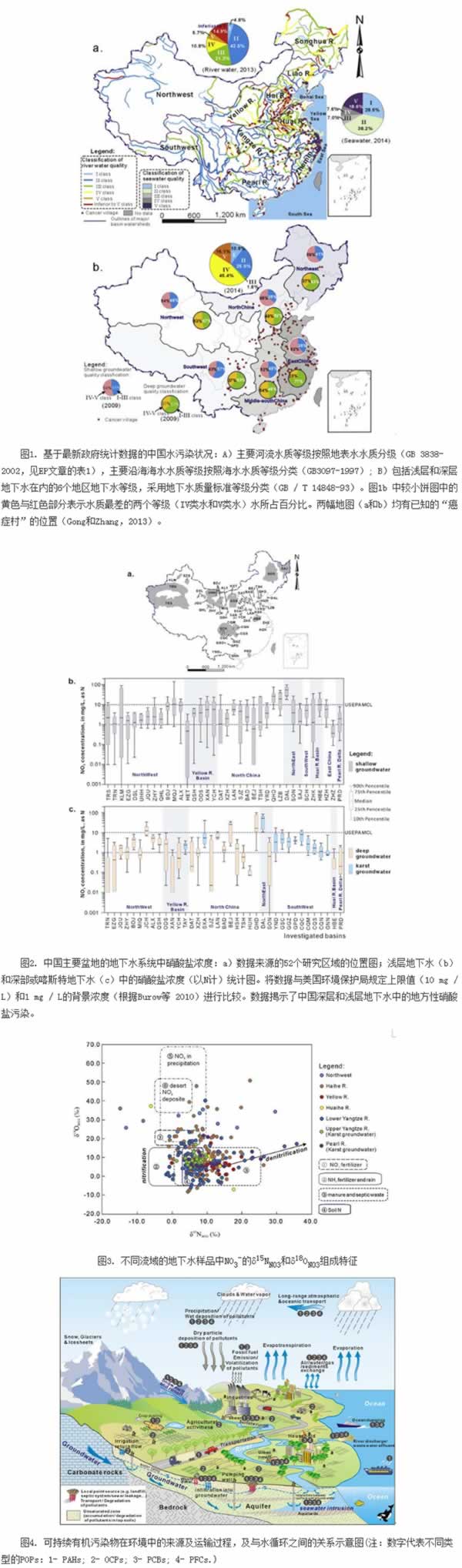
Geographical resources have made progress in research on water pollution in China