The implantation of chips into the human body is no longer an illusion. How long can human "superman" dreams be realized? Recently, researchers at Columbia University in New York developed a chip that can use organic compounds to convert electricity into electricity. This compound is known as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Students who have studied biology probably know that this substance is a direct source of energy for biological cells. It is understood that the core of this new technology is to combine an ordinary CMOS (solid complementary metal oxide semiconductor) integrated circuit with an artificial lipid bilayer membrane with an ATP-powered ion pump. After the combination of the two, although it is impossible to achieve biological characteristics, CMOS integrated circuits can draw energy from the ATP like cells (fully in accordance with the law of conservation of energy). The specific point will be that they help ATP deliver energy to the chip through the ATPase that is separated from the cells. The efficiency of this chemical energy conversion to electricity is 14.9%. At present, the research team has developed a prototype of a few millimeters to verify this function. The significance of this technology is that implanted chips and other medical devices will not be affected by battery problems in the body. However, this technique also has a drawback. Because ATP exists only in the interior of cells, it cannot be applied to ordinary mobile medical devices such as pacemakers. The team leader Ken Shepard said that currently available implantable technologies use passive components with very limited capabilities, but they have more ambitious goals—to make the implanted devices computationally even more complex. The function. Three Row Paint Brush,Brush Oil Photoshop,Brushes Medibang Paint,Fence Paint Brush Laizhou Chenke trading Co., Ltd. , https://www.chenkegroup.com
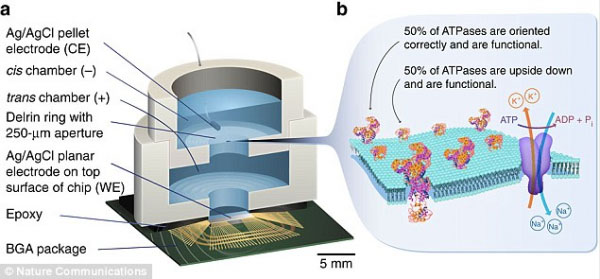
Scientists Discover New Bioenergy to Power Chips