[China Aluminum Network] Aluminum and aluminum alloy materials have low density, high strength, high thermal conductivity, strong corrosion resistance, good physical properties and mechanical properties, and are therefore widely used in welded structures of industrial products. For a long time, due to improper selection of welding methods and welding process parameters, aluminum alloy parts have been severely deformed due to excessive stress concentration after welding, or due to defects such as pores, slag, and incomplete penetration of welds, resulting in weld metal cracks or materials. Loosening has seriously affected product quality and performance.
Single Sphere Type
Hot Water, Oil, Acid, Alkali.
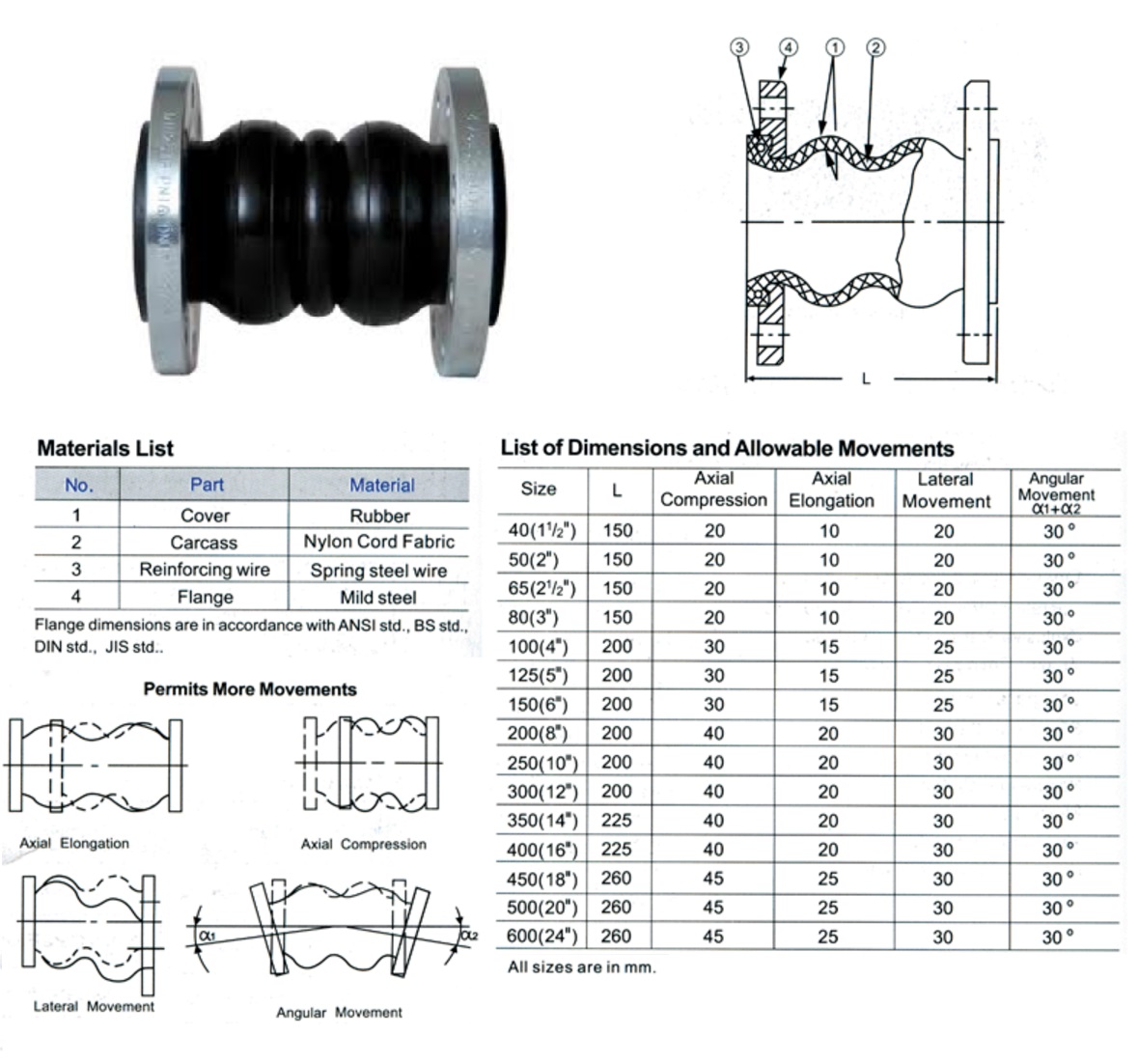
Double Sphere Type
Operating Conditions :
Flange Type Rubber Expansion Joint Flange Type Rubber Expansion Joint,Flange Rubber Joint,Flange Expansion Joint,Flange Rubber Bridge Expansion Joint HEBEI ZIFENG NEW ENERGY TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD. , https://www.zifengpipeline.com
1 Aluminum alloy material characteristics Aluminum is a silver-white light metal, with good plasticity, high electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity, but also has the ability to resist oxidation and corrosion. Aluminum is easily oxidized to produce a thin film of Al2O3, which can easily cause inclusions in the welds, thereby destroying the continuity and uniformity of the metal and reducing its mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. Common chemical composition and mechanical properties of aluminum alloy base metal and welding wire. Guang Yirong copper and aluminum wholesale.
2 welding difficulties of aluminum alloy materials (1) easily oxidized. In the air, aluminum is easily oxidized to form a dense Al 2 O 3 thin film (thickness of about 0.1-0.2 μm) and a high melting point (about 2050°C) far beyond the melting point of aluminum and its alloys (approximately 600°C or so). . The density of alumina is 3.95-4.10g/cm3, which is about 1.4 times that of aluminum. The surface of alumina film easily absorbs moisture. When welding, it impedes the fusion of the base metal, and it is easy to form defects such as pores, inclusions, and fusion. Causes drop in weld performance.
(2) easy to produce pores. The main reason for the generation of pores during the welding of aluminum and aluminum alloys is hydrogen. Since liquid aluminum can dissolve a large amount of hydrogen, while solid aluminum hardly dissolves hydrogen, when the bath temperature rapidly cools and solidifies, hydrogen is too late to escape, and it is easy to weld. Slots form in the seams. Hydrogen pores are difficult to completely avoid at present, and there are many sources of hydrogen, such as hydrogen in the arc welding atmosphere, moisture adsorbed on the surface of the aluminum plate and the welding wire, and the like. Practice has proved that even if the argon gas meets the requirements of GB/T4842, the purity reaches 99.99%, but when the moisture content reaches 20ppm, a large number of dense pores will also appear. When the relative humidity of the air exceeds 80%, the weld will clearly appear. Stoma.
(3) The weld deformation and crack formation tend to be large. The coefficient of linear expansion and crystal shrinkage of aluminum are approximately twice as large as those of steel, and the internal stress of the large welding deformation is easily generated, and the structure with greater rigidity will promote the generation of hot cracks.
(4) The thermal conductivity of aluminum is large (pure aluminum 0.538 card/Cm.s. °C). About four times that of steel, welding aluminum and aluminum alloys consumes more heat than welding steel.
(5) Evaporation loss of alloying elements. Aluminum alloys contain low-boiling elements (such as magnesium, zinc, manganese, etc.), which can easily evaporate and burn under high-temperature arcs, thereby changing the chemical composition of the weld metal and deteriorating the weld performance.
(6) High temperature strength and low plasticity. Aluminum has low strength and plasticity at high temperatures, which destroys the formation of the weld metal and sometimes causes the weld metal to fall down and wear through.
(7) No color change. When aluminum and aluminum alloys change from a solid state to a liquid state, there is no noticeable color change, making it difficult for operators to grasp the heating temperature.
(3) Welding method of aluminum alloy materials (1) Prepare pre-weld chemical or mechanical methods and strictly clean the surface oxide films on both sides of the weld bevel.
Chemical cleaning is the use of alkali or acid cleaning the surface of the workpiece, the method can remove the oxide film, but also remove oil, the specific process is as follows: volume fraction of 6% to 10% sodium hydroxide solution, soaked at 70 °C for about 0.5min → Washing → Nitric acid with a volume fraction of 15% is soaked at room temperature for 1 minute for neutralization → water washing → warm water washing → drying. The surface of the aluminum alloy after washing is matt silver white.
Mechanical cleaning can be pneumatic or electric milling cutters. Scrapers, trowels and other tools can also be used. For thinner oxide films, 0.25mm copper wire brush can also be used to remove the oxide film.
Welding is performed immediately after cleaning. If it is left for more than 4 hours, it should be cleaned again.
(2) Determine the assembly clearance and the positioning welding distance During the welding process, the aluminum plate is heated to expand, so that the weld groove gap is reduced. If the assembly gap before welding is too small, the overlap between the two plates will be caused during the welding process. Increase the surface roughness and deformation after welding; on the contrary, if the assembly gap is too large, the welding will be difficult and burn-through may occur. The proper tack gap can guarantee the required tack gap. Therefore, choosing an appropriate assembly gap and tack gap is an effective measure to reduce deformation. According to experience, the reasonable assembly process parameters for different seam thicknesses are shown in Table 2.
(3) Selection of welding equipment There are many kinds of welding products on the market at present. Under normal circumstances, tungsten tungsten arc welding (TIG welding) should be adopted. It is a welding method that melts the base metal and the filler wire with the arc heat generated by the tungsten electrode and the workpiece under the protection of the argon gas. When the welder is working, since the polarity of the alternating current is periodically changed, the half wave is a direct current connection and the half wave is a direct current reverse connection in each cycle. The tungsten electrode can emit enough electrons without overheating during the half wave period that is connected, which is beneficial to the stability of the arc. The oxide film formed on the surface of the work piece during the half wave period of reverse welding is easily cleaned to obtain a bright, beautiful, well-formed weld seam.
(4) Select the wire generally use 301 pure aluminum wire and 311 aluminum silicon wire.
(5) The welding method and parameters are generally selected by the left welding method. The welding torch and the workpiece are at an angle of 60°. When the welding thickness is 15mm or more, the right welding method is used, and the welding torch and the workpiece are at a 90° angle.
When the welding wall thickness is more than 3mm, open V-shaped groove, the included angle is 60 ° ~ 70 °, the gap should not be greater than 1mm, to complete the multilayer welding. When the wall thickness is less than 1.5mm, no groove, no clearance, no filler wire. When welding fixed pipe butt joints, when the pipe diameter is 200mm and the wall thickness is 6mm, a tungsten electrode with a diameter of 3 to 4mm, a welding current of 220 to 240A, a filler wire of 4mm in diameter, and 1 to 2 layers shall be used. After welding.
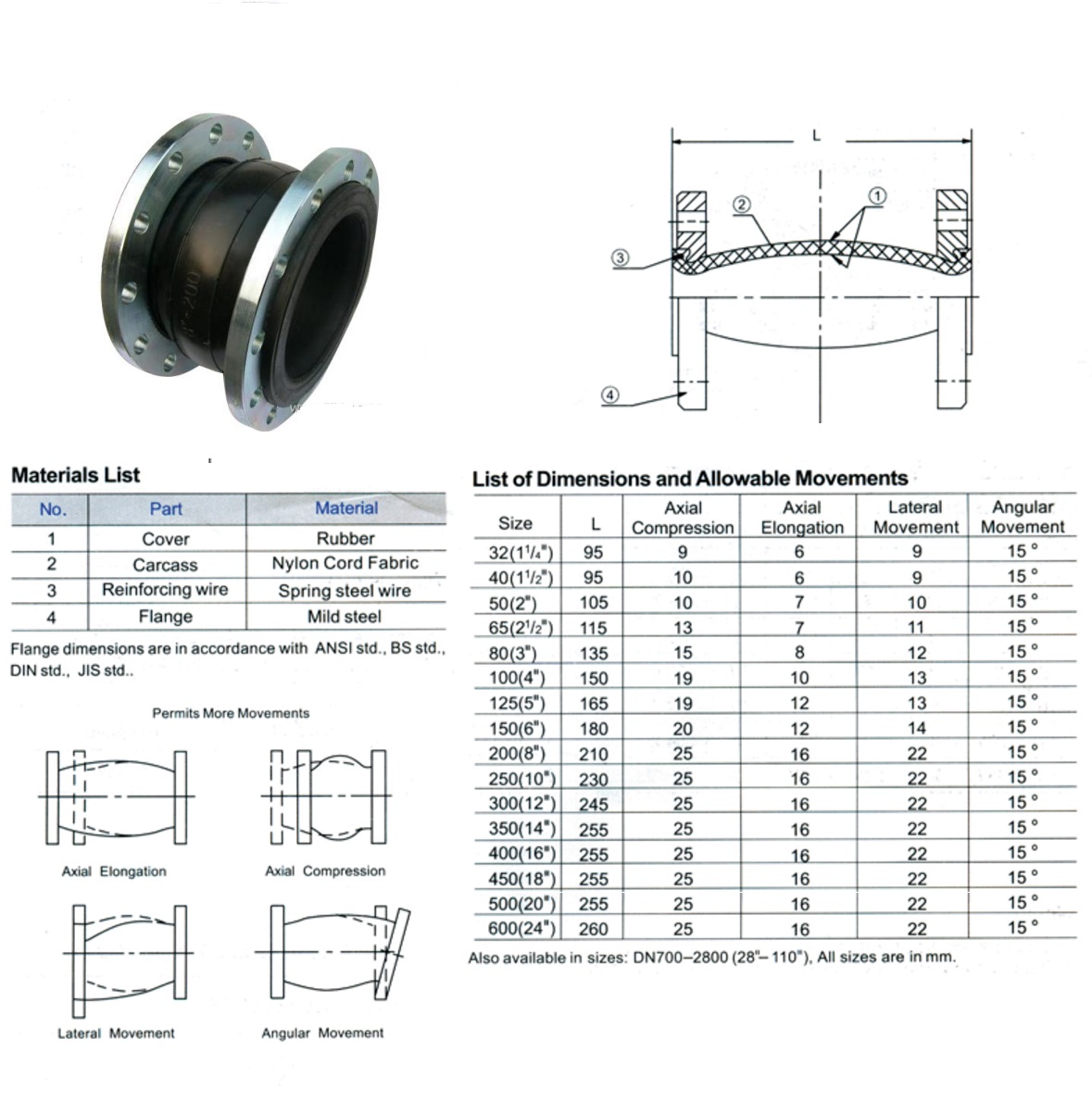
Operating Pressure:PN10/PN16
Explosive Pressure:3.0/4.5Mpa
Vacuum Rating:400/650/750 mmHg
Temperature :
EPDM:-10℃ to 120 ℃
NBR:-10℃ to 82℃
Neoprene:-10℃ to 110℃
Medium :
Air, Water, Sea Water,
Hot Water, Oil, Acid, Alkali.
Aluminum and aluminum alloy parts welding process
Operating Conditions :
Operating Pressure:PN10/PN16
Explosive Pressure:3.0/4.5Mpa
Vacuum Rating:400/650/750 mmHg
Temperature :
EPDM:-10℃ to 120 ℃
NBR:-10℃ to 82℃
Neoprene:-10℃ to 110℃
Medium :
Air, Water, Sea Water,