According to foreign media theVerge reports, there are many claims about lithium and cobalt in battery materials, but some chemists believe that the future battery can be powered by a commonly used dye. This fuel is methylene blue, which has a strong sapphire color. Although this fuel looks pretty, it becomes a harmful substance when it seeps into the wastewater from the textile mill. Anjula Kosswattaarachchi, a PhD student in chemistry at the University of Buffalo, once worked in textile-related work at the Institute of Nanotechnology in Sri Lanka, so she is very familiar with the pollution of methylene blue. During the time at the University of Buffalo, Kosswattaarachchi studied a liquid battery called a "flow battery", and she was also involved in a project dedicated to removing harmful substances from wastewater. At that time, she came up with an idea to combine these two concepts, and since then has been working on whether methylene blue wastewater can provide energy for these liquid batteries. At present, the research is still in the early stages, and the research team has not studied the real wastewater, but this may indeed be a two-for-one approach. In this regard, theVerge talked to Kosswattaarachchi about why methylene blue is a problem and how it can become a battery solution. The following are the main interview contents organized by theVerge: Q: Tell me about methylene blue. Is it common? Is it poisonous? Why use it if it is poisonous? A: We use it because it can produce a specific color. It is one of the most commonly used fuels. It can even be used as a drug with an appropriate dose. But such an appropriate dose is difficult to obtain, and in this case it becomes toxic. It can cause diseases including cancer and genetic mutations. It can also cause damage to the environment because the dye is easy to see even at very low concentrations. So when it is added, the penetration of sunlight will be blocked, which damages photosynthesis. It may be the most studied dye when studying how to remove it from water. Q: So your idea is to use wastewater containing methylene blue in mobile batteries, right? Rather than extracting the dye from the water, how about reusing the water to power the battery? A: Yes. Q: Can you explain what a mobile battery is? A: Simply put, it is two external containers that hold liquid electrolyte. The electrolyte is pumped through the center, and then a chemical reaction occurs to power the battery. This is a relatively new area of ​​research, but the advantage of mobile batteries is safety. They are liquid, so they will not catch fire. Containers can be large, so you can power many things on a large scale. They can store energy longer. Q: Where will methylene blue be added? A: Methylene blue is part of the liquid we will store and pump into the container. Normally, you have to add salt to the solution to make a chemical reaction. Methylene blue already contains salt in wastewater. Q: So what did you find in the experiment? A: In the experiment, we made a small battery with methylene dye added to the brine. It can be used 50 times on one charge. It is also quite stable. We calculated that when methylene blue is used as a component of the battery, we can produce 9.6 kilojoules per liter. In fact, methylene must be combined with another material, so we are still studying this material. In addition, we still need to use real wastewater samples for testing. This is the next step. Piercing Screwdriver,Magnetic Screwdriver,Slotted And Phillips Screwdriver,Reversible Dual End Screwdriver Yucheng Weisite Measuring Tools Co., Ltd , https://www.wsttools.com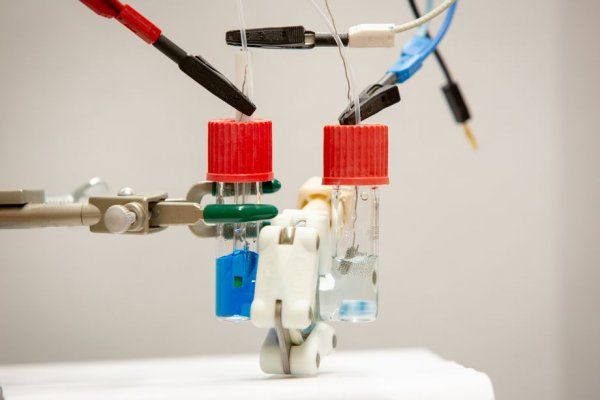
Researchers found that blue dye in wastewater can power batteries